Product Description
Rotary hermetic compressors use the rotating action of a roller inside a cylinder to compress the refrigerant.
Rotaries, by design, include less parts than other types of compression technology and provide an alternative,
efficient option for various applications.
High efficiency CHINAMFG rotary compressors provide enhanced reliability, reduced sound and maximum flexibility with vertical and horizontal installation options for air conditioning and refrigeration applications.
Today’s modern air conditioning and commercial refrigeration applications require high efficiency combined with the ability to utilize more eco-friendly refrigerants. CHINAMFG rotary compressors continue to lead the way.
Applicaiton:
Truck sleeper air conditioner
Electric vehicle air conditioning system
truck air conditioner
vehicle air conditioner with electric compressor
electric vehicle air conditioner
special vehicle air conditioner
vessel air conditioner
heat pump air conditioner
solar air conditioner
telecom-shelter air conditioner, etc.
| After-sales Service: | None |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12m |
| Classification: | Variable Capacity |
| Job Classification: | Rotary Type |
| Transmission Power: | Dynamoelectric |
| Cooling Method: | Air-cooled |
| Samples: |
US$ 265/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
.webp)
Are there special considerations for air compressor installations in remote areas?
Yes, there are several special considerations to take into account when installing air compressors in remote areas. These areas often lack access to infrastructure and services readily available in urban or well-developed regions. Here are some key considerations:
1. Power Source:
Remote areas may have limited or unreliable access to electricity. It is crucial to assess the availability and reliability of the power source for operating the air compressor. In some cases, alternative power sources such as diesel generators or solar panels may need to be considered to ensure a consistent and uninterrupted power supply.
2. Environmental Conditions:
Remote areas can present harsh environmental conditions that can impact the performance and durability of air compressors. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, dust, and corrosive environments may require the selection of air compressors specifically designed to withstand these conditions. Adequate protection, insulation, and ventilation must be considered to prevent damage and ensure optimal operation.
3. Accessibility and Transport:
Transporting air compressors to remote areas may pose logistical challenges. The size, weight, and portability of the equipment should be evaluated to ensure it can be transported efficiently to the installation site. Additionally, the availability of suitable transportation infrastructure, such as roads or air transportation, needs to be considered to facilitate the delivery and installation process.
4. Maintenance and Service:
In remote areas, access to maintenance and service providers may be limited. It is important to consider the availability of trained technicians and spare parts for the specific air compressor model. Adequate planning for routine maintenance, repairs, and troubleshooting should be in place to minimize downtime and ensure the longevity of the equipment.
5. Fuel and Lubricants:
For air compressors that require fuel or lubricants, ensuring a consistent and reliable supply can be challenging in remote areas. It is necessary to assess the availability and accessibility of fuel or lubricant sources and plan for their storage and replenishment. In some cases, alternative or renewable fuel options may need to be considered.
6. Noise and Environmental Impact:
Remote areas are often characterized by their natural beauty and tranquility. Minimizing noise levels and environmental impact should be a consideration when installing air compressors. Selecting models with low noise emissions and implementing appropriate noise reduction measures can help mitigate disturbances to the surrounding environment and wildlife.
7. Communication and Remote Monitoring:
Given the remote location, establishing reliable communication channels and remote monitoring capabilities can be essential for effective operation and maintenance. Remote monitoring systems can provide real-time data on the performance and status of the air compressor, enabling proactive maintenance and troubleshooting.
By addressing these special considerations, air compressor installations in remote areas can be optimized for reliable operation, efficiency, and longevity.
.webp)
What safety precautions should be taken when working with compressed air?
Working with compressed air requires adherence to certain safety precautions to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of individuals involved. Here are some important safety measures to consider:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate PPE, including safety goggles or a face shield to protect eyes from flying debris or particles, hearing protection to reduce noise exposure, and gloves to safeguard hands from potential hazards.
2. Compressed Air Storage:
Avoid storing compressed air in containers that are not designed for this purpose, such as soda bottles or makeshift containers. Use approved and properly labeled air storage tanks or cylinders that can handle the pressure and are regularly inspected and maintained.
3. Pressure Regulation:
Ensure that the air pressure is regulated to a safe level suitable for the equipment and tools being used. High-pressure air streams can cause serious injuries, so it is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and never exceed the maximum allowable pressure.
4. Air Hose Inspection:
Regularly inspect air hoses for signs of damage, such as cuts, abrasions, or leaks. Replace damaged hoses immediately to prevent potential accidents or loss of pressure.
5. Air Blowguns:
Exercise caution when using air blowguns. Never direct compressed air towards yourself or others, as it can cause eye injuries, hearing damage, or dislodge particles that may be harmful if inhaled. Always point blowguns away from people or any sensitive equipment or materials.
6. Air Tool Safety:
Follow proper operating procedures for pneumatic tools. Ensure that tools are in good working condition, and inspect them before each use. Use the appropriate accessories, such as safety guards or shields, to prevent accidental contact with moving parts.
7. Air Compressor Maintenance:
Maintain air compressors according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Regularly check for leaks, clean or replace filters, and drain moisture from the system. Proper maintenance ensures the safe and efficient operation of the compressor.
8. Training and Education:
Provide adequate training and education to individuals working with compressed air. Ensure they understand the potential hazards, safe operating procedures, and emergency protocols. Encourage open communication regarding safety concerns and implement a culture of safety in the workplace.
9. Lockout/Tagout:
When performing maintenance or repairs on compressed air systems, follow lockout/tagout procedures to isolate the equipment from energy sources and prevent accidental startup. This ensures the safety of the individuals working on the system.
10. Proper Ventilation:
Ensure proper ventilation in enclosed areas where compressed air is used. Compressed air can displace oxygen, leading to a potential risk of asphyxiation. Adequate ventilation helps maintain a safe breathing environment.
By adhering to these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with compressed air and create a safer work environment.
.webp)
What are the different types of air compressors?
There are several different types of air compressors, each with its own unique design and operating principle. Here’s an overview of the most commonly used types:
1. Reciprocating Air Compressors: Reciprocating air compressors, also known as piston compressors, use one or more pistons driven by a crankshaft to compress air. They operate by drawing air into a cylinder, compressing it with the piston’s up-and-down motion, and discharging the compressed air into a storage tank. Reciprocating compressors are known for their high pressure capabilities and are commonly used in industrial applications.
2. Rotary Screw Air Compressors: Rotary screw air compressors utilize two interlocking screws to compress air. As the male and female screws rotate, the air is trapped between them and gradually compressed as it moves along the screw threads. These compressors are known for their continuous duty cycle, high efficiency, and quiet operation. They are widely used in industrial, commercial, and automotive applications.
3. Centrifugal Air Compressors: Centrifugal air compressors rely on the principle of centrifugal force to compress air. They use a high-speed impeller to accelerate the incoming air and then convert the kinetic energy into pressure energy. Centrifugal compressors are commonly used in large-scale industrial applications that require high volumes of compressed air.
4. Rotary Vane Air Compressors: Rotary vane air compressors employ a rotor with sliding vanes that compress the air. As the rotor rotates, the vanes slide in and out of the rotor, creating compression chambers. Air is drawn in, trapped, and compressed as the vanes move. These compressors are compact, reliable, and suitable for small to medium-sized applications.
5. Axial Flow Air Compressors: Axial flow air compressors are primarily used in specialized applications such as aircraft engines and gas turbines. They utilize a series of rotating and stationary blades to compress air in a continuous flow. Axial flow compressors are known for their high flow rates and are designed for applications that require large volumes of compressed air.
6. Scroll Air Compressors: Scroll air compressors consist of two interlocking spirals or scrolls that compress the air. One spiral remains stationary while the other orbits around it, creating a series of expanding and contracting pockets that compress the air. Scroll compressors are compact, reliable, and commonly used in applications where low noise and oil-free air are required, such as medical and dental equipment.
These are just a few examples of the different types of air compressors available. Each type has its own advantages, capabilities, and ideal applications. The choice of air compressor depends on factors such as required pressure, flow rate, duty cycle, noise level, oil-free operation, and specific application requirements.


editor by CX 2023-10-05
China Mitsubishi R134A Mini Rotary Compressor Kb122ypd for Precision Cabinet Air Condition air compressor parts
Product Description
Mitsubishi R134a Mini Rotary Compressor KB122YPD for Precision Cupboard Air Issue
Specialized Specification
Complex Specification for other Collection
A lot more Power range for picking a piston refrigeration compressor
| Model | CB150 | CB32 | CB40 | CB50 | CB64 | CB80 | CB90 | CB100 | CB125 | ||
| Nominal electricity | KW | 10.eight | one.8 | 2.5 | 3.seventy five | three.75 | 5.five | 6.5 | 7.5 | nine.8 | |
| Refrigerating potential | 50HZ | Kcal/H | 38000 | 6700 | 9100 | 12600 | 14600 | 18500 | 21600 | 25600 | 32700 |
| BTU/H | 150800 | 26600 | 36100 | 50000 | 57900 | 73400 | 85700 | 101600 | 129800 | ||
| 60HZ | Kcal/H | 44700 | 8000 | 11200 | 15000 | 17700 | 21800 | 25800 | 35710 | 38400 | |
| BTU/H | 177400 | 31700 | 44400 | 59520 | 75710 | 86500 | 99600 | 119400 | 152400 | ||
| Input electricity | W | 50HZ | 14200 | 2520 | 3440 | 4640 | 5530 | 6570 | 7900 | 9320 | 12000 |
| 60HZ | 18000 | 3120 | 4280 | 5760 | 7571 | 8030 | 9800 | 11350 | 15200 | ||
| Work current | A | 50HZ | 47 | eight.6 | twelve.seven | 17 | 19.three | 21.eight | twenty five.one | 31.four | 38.5 |
| 60HZ | fifty four | nine.eight | thirteen.5 | 17.eight | 21.8 | 24 | 29.six | 35.1 | 45.6 | ||
| Discharge price | cc | 286.four | 58.eight | 77.9 | 101.2 | 117.4 | 151.7 | 178.9 | 202 | 249.9 | |
| cu. In | seventeen.48 | three.59 | four.75 | six.18 | seven.sixteen | 9.26 | ten.92 | 12.33 | 15.twenty five | ||
| EER | 50HZ | Kcal/H | 2.68 | two.sixty six | 2.65 | two.seventy four | 2.sixty four | 2.eighty two | two.73 | 2.75 | two.seventy three |
| BTU/H | 10.six | 10.6 | 10.5 | 10.9 | 10.5 | eleven.2 | 10.eight | ten.nine | ten.8 | ||
| 60HZ | Kcal/H | 2.forty nine | 2.56 | 2.62 | 2.sixty three | 2.fifty two | two.seventy one | two.fifty six | two.65 | two.53 | |
| BTU/H | nine.9 | ten.two | ten.4 | 10.4 | 10 | 10.eight | 10.two | 10.five | 10 | ||
| Noise | dB(A) | 50HZ | 73 | sixty seven | sixty nine | seventy two | 71 | 75 | 76 | 78 | 80 |
| 60HZ | seventy three | 69 | 72 | 72 | 73 | 76 | 78 | 78 | 80 | ||
| Fat | kg | seventy three.one | 38 | 40 | 43 | forty three | 63.6 | 63.six | sixty six.1 | 69.one | |
| Insulation grade | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | ||
| Starting present | A | 50HZ | 330 | 76 | 112 | 157 | 157 | 200 | 200 | 225 | 292 |
| 60HZ | 290 | seventy one | 102 | 148 | 148 | one hundred eighty | a hundred and eighty | 195 | 265 | ||
| Admission pipe dia. | mm | 28 | 15.88 | 15.88 | 22 | 22 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 | |
| inch | one | 5/eight | 5/eight | 7/eight | 7/eight | 1 | one | one | 1 | ||
| Vent-pipe dia. | mm | 19.05 | nine.52 | nine.fifty two | 12.7 | twelve.seven | 19.05 | 19.05 | 19.05 | 19.05 | |
| inch | 3/four | 3/eight | 3/8 | 1/two | 1/two | 3/four | 3/four | 3/4 | 3/4 | ||
Refrigeration Compressors Scope
We are specialised in refrigeration compressors, including rotary, scroll, piston, screw, airtight, semi-airtight all types of brand names of refrigeration compressors.
1. Rotary compressor: Toshiba,Panasonic, CZPT LG
2. Scroll compressor: Copeland,Dan-foss performer,Hitachi,Daikin,Sanyo
three.Piston airtight compressor:Tecumseh CZPT MT,NTZ,MTZ series.
4.Semi-hermetic Reciprocating Compressor:Copeland,Bit-zer,Provider
5.Screw compressor :Little bit-zer ,Hitachi
Mitsubishi R134a Mini Rotary Compressor KB122YPD for Precision Cupboard Air Situation
Brand Variety
Mitsubishi R134a Mini Rotary Compressor KB122YPD for Precision Cabinet Air Condition
Workshop
FAQ
1. What is the cost for a refrigeration compressor?
The price is made a decision by Quantity.
2. How about samples?
Sample Direct Time: 5 working days
Sample Price:
1). It really is free of charge for all for a standard consumer
2). For new consumers, we will demand first, it is totally refundable when the purchase is confirmed.
3. How a lot of times for shipping and delivery?
Delivery Techniques and Lead Time:
By Express: 3-5 operating days to your doorway (DHL, UPS, TNT, FedEx…)
By Air: 5-8 functioning times to your airport
By Sea: Pls suggest your port of location, the specific times will be verified by our forwarders, and the adhering to guide time is for your reference. Europe and America (25 – 35 times), Asia (3-7 days), Australia ( 16-23 times)
four. What are the Terms of Payment?
Credit rating Card, T/T, L/C, Western Union 30% T/T in progress, 70% ahead of supply.
5. Packaging & Shipping?
Pallet, wood case or with outer carton, or as customers’ specific demands.
6. Why decide on your company?
We are focusing on all factors of refrigeration compressors, substantial top quality, and good costs.
We strictly implement the rules according to the quality standard in every aspect from the purchase of uncooked materials to the manufacturing method and outgoing of goods.
Excellent support and Excellent good quality is offered all the time…
Packaging & Shipping Packing: Carton, picket box, and pallet, or as for every customers’ needs.
Transport: By Categorical (DHL /UPS /TNT /FedEx /EMS), By Air, By Sea
Mitsubishi R134a Mini Rotary Compressor KB122YPD for Precision Cupboard Air Issue
Packaging and shipping and delivery
HVAC&R Exhibition
Mitsubishi R134a Mini Rotary Compressor KB122YPD for Precision Cabinet Air Problem
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 6 Months |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Parallel Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Model | CB150 | CB32 | CB40 | CB50 | CB64 | CB80 | CB90 | CB100 | CB125 | ||
| Nominal power | KW | 10.8 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 3.75 | 3.75 | 5.5 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 9.8 | |
| Refrigerating capacity | 50HZ | Kcal/H | 38000 | 6700 | 9100 | 12600 | 14600 | 18500 | 21600 | 25600 | 32700 |
| BTU/H | 150800 | 26600 | 36100 | 50000 | 57900 | 73400 | 85700 | 101600 | 129800 | ||
| 60HZ | Kcal/H | 44700 | 8000 | 11200 | 15000 | 17700 | 21800 | 25800 | 30100 | 38400 | |
| BTU/H | 177400 | 31700 | 44400 | 59520 | 70200 | 86500 | 99600 | 119400 | 152400 | ||
| Input power | W | 50HZ | 14200 | 2520 | 3440 | 4640 | 5530 | 6570 | 7900 | 9320 | 12000 |
| 60HZ | 18000 | 3120 | 4280 | 5760 | 7020 | 8030 | 9800 | 11350 | 15200 | ||
| Work current | A | 50HZ | 47 | 8.6 | 12.7 | 17 | 19.3 | 21.8 | 25.1 | 31.4 | 38.5 |
| 60HZ | 54 | 9.8 | 13.5 | 17.8 | 21.8 | 24 | 29.6 | 35.1 | 45.6 | ||
| Discharge rate | cc | 286.4 | 58.8 | 77.9 | 101.2 | 117.4 | 151.7 | 178.9 | 202 | 249.9 | |
| cu. In | 17.48 | 3.59 | 4.75 | 6.18 | 7.16 | 9.26 | 10.92 | 12.33 | 15.25 | ||
| EER | 50HZ | Kcal/H | 2.68 | 2.66 | 2.65 | 2.74 | 2.64 | 2.82 | 2.73 | 2.75 | 2.73 |
| BTU/H | 10.6 | 10.6 | 10.5 | 10.9 | 10.5 | 11.2 | 10.8 | 10.9 | 10.8 | ||
| 60HZ | Kcal/H | 2.49 | 2.56 | 2.62 | 2.63 | 2.52 | 2.71 | 2.56 | 2.65 | 2.53 | |
| BTU/H | 9.9 | 10.2 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 10 | 10.8 | 10.2 | 10.5 | 10 | ||
| Noise | dB(A) | 50HZ | 73 | 67 | 69 | 72 | 71 | 75 | 76 | 78 | 80 |
| 60HZ | 73 | 69 | 72 | 72 | 73 | 76 | 78 | 78 | 80 | ||
| Weight | kg | 73.1 | 38 | 40 | 43 | 43 | 63.6 | 63.6 | 66.1 | 69.1 | |
| Insulation grade | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | ||
| Starting current | A | 50HZ | 330 | 76 | 112 | 157 | 157 | 200 | 200 | 225 | 292 |
| 60HZ | 290 | 71 | 102 | 148 | 148 | 180 | 180 | 195 | 265 | ||
| Admission pipe dia. | mm | 28 | 15.88 | 15.88 | 22 | 22 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 | |
| inch | 1 | 5/8 | 5/8 | 7/8 | 7/8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Vent-pipe dia. | mm | 19.05 | 9.52 | 9.52 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 19.05 | 19.05 | 19.05 | 19.05 | |
| inch | 3/4 | 3/8 | 3/8 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | ||
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 6 Months |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Parallel Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Model | CB150 | CB32 | CB40 | CB50 | CB64 | CB80 | CB90 | CB100 | CB125 | ||
| Nominal power | KW | 10.8 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 3.75 | 3.75 | 5.5 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 9.8 | |
| Refrigerating capacity | 50HZ | Kcal/H | 38000 | 6700 | 9100 | 12600 | 14600 | 18500 | 21600 | 25600 | 32700 |
| BTU/H | 150800 | 26600 | 36100 | 50000 | 57900 | 73400 | 85700 | 101600 | 129800 | ||
| 60HZ | Kcal/H | 44700 | 8000 | 11200 | 15000 | 17700 | 21800 | 25800 | 30100 | 38400 | |
| BTU/H | 177400 | 31700 | 44400 | 59520 | 70200 | 86500 | 99600 | 119400 | 152400 | ||
| Input power | W | 50HZ | 14200 | 2520 | 3440 | 4640 | 5530 | 6570 | 7900 | 9320 | 12000 |
| 60HZ | 18000 | 3120 | 4280 | 5760 | 7020 | 8030 | 9800 | 11350 | 15200 | ||
| Work current | A | 50HZ | 47 | 8.6 | 12.7 | 17 | 19.3 | 21.8 | 25.1 | 31.4 | 38.5 |
| 60HZ | 54 | 9.8 | 13.5 | 17.8 | 21.8 | 24 | 29.6 | 35.1 | 45.6 | ||
| Discharge rate | cc | 286.4 | 58.8 | 77.9 | 101.2 | 117.4 | 151.7 | 178.9 | 202 | 249.9 | |
| cu. In | 17.48 | 3.59 | 4.75 | 6.18 | 7.16 | 9.26 | 10.92 | 12.33 | 15.25 | ||
| EER | 50HZ | Kcal/H | 2.68 | 2.66 | 2.65 | 2.74 | 2.64 | 2.82 | 2.73 | 2.75 | 2.73 |
| BTU/H | 10.6 | 10.6 | 10.5 | 10.9 | 10.5 | 11.2 | 10.8 | 10.9 | 10.8 | ||
| 60HZ | Kcal/H | 2.49 | 2.56 | 2.62 | 2.63 | 2.52 | 2.71 | 2.56 | 2.65 | 2.53 | |
| BTU/H | 9.9 | 10.2 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 10 | 10.8 | 10.2 | 10.5 | 10 | ||
| Noise | dB(A) | 50HZ | 73 | 67 | 69 | 72 | 71 | 75 | 76 | 78 | 80 |
| 60HZ | 73 | 69 | 72 | 72 | 73 | 76 | 78 | 78 | 80 | ||
| Weight | kg | 73.1 | 38 | 40 | 43 | 43 | 63.6 | 63.6 | 66.1 | 69.1 | |
| Insulation grade | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | E | ||
| Starting current | A | 50HZ | 330 | 76 | 112 | 157 | 157 | 200 | 200 | 225 | 292 |
| 60HZ | 290 | 71 | 102 | 148 | 148 | 180 | 180 | 195 | 265 | ||
| Admission pipe dia. | mm | 28 | 15.88 | 15.88 | 22 | 22 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 | |
| inch | 1 | 5/8 | 5/8 | 7/8 | 7/8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Vent-pipe dia. | mm | 19.05 | 9.52 | 9.52 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 19.05 | 19.05 | 19.05 | 19.05 | |
| inch | 3/4 | 3/8 | 3/8 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | ||
Choosing the Right Air Compressor For Your Home
You will find that air compressors are indispensable tools for a variety of situations, including garages, home workshops, and basements. These tools can power a variety of tools, and each model is sized to suit the job at hand. Because air compressors have only one motor, they are lightweight, compact, and easy to handle. Using one air compressor to power several tools will also reduce the wear and tear on individual components. This article will introduce some important characteristics to look for when choosing the right air compressor for your home.
Positive displacement
A positive displacement compressor applies pressure to a fluid, whereas a centrifugal one does the opposite. A positive displacement compressor creates the desired pressure by trapping air and increasing its volume. Its discharge valve releases the high-pressure gas. These compressors are used in industrial applications and nuclear power plants. The difference between a positive and negative displacement compressor is that a positive displacement compressor can compress and release air at a consistent rate.
A positive displacement air compressor uses a reciprocating piston to compress air. This reduces the volume of the air in the compression chamber, and a discharge valve opens when the pressure reaches the desired level. These compressors are used in bicycle pumps and other pneumatic tools. Positive displacement air compressors have multiple inlet ports and have several configurations. Positive displacement air compressors have a single-acting and double-acting piston, and can be oil-lubricated or oil-free.
A positive displacement air compressor is different from a dynamic compressor. It draws air into the compression chambers and then releases the pressure when the valve is opened. Positive displacement compressors are common in industrial applications and are available in single-acting, double-acting, and oil-lubricated models. Large piston compressors have ventilated intermediate pieces and crossheads on gudgeon pins. Smaller models have permanently sealed crankcases with bearings.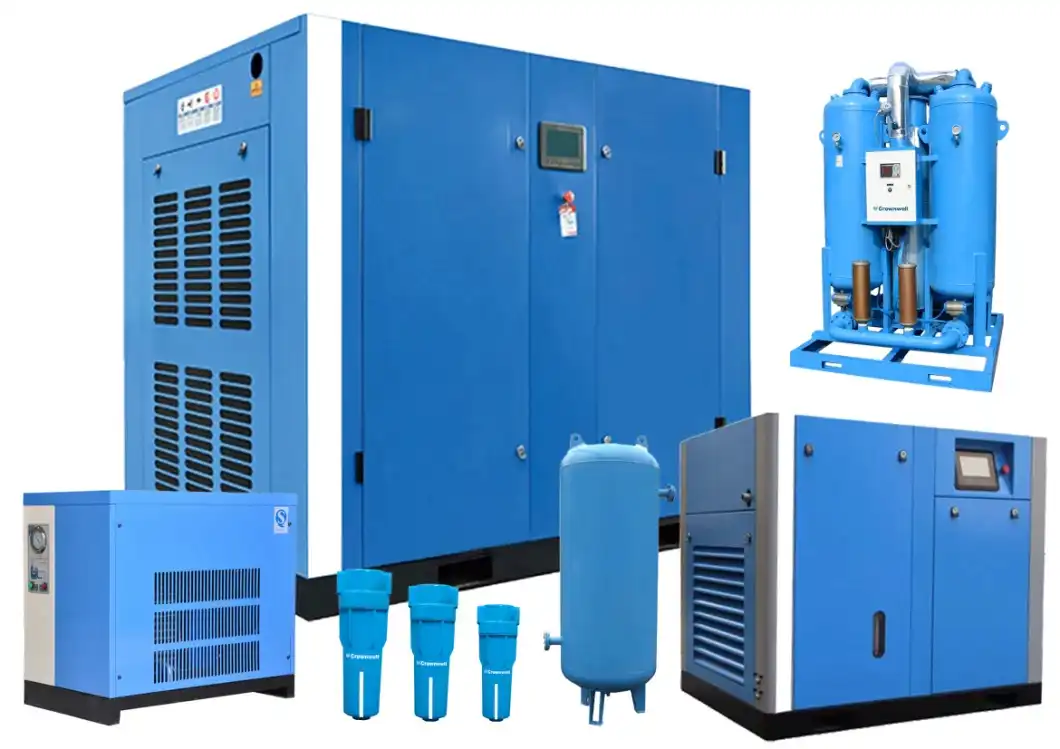
Oil-free
Oil-free air compressors have some advantages over their oil-lubricated counterparts. They do not require lubrication oil because they are coated with Teflon. The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction and is layered, so it slides past other layers with little effort. Because of this, oil-free compressors tend to be cheaper and still deliver comparable performance. Oil-free compressors are a good choice for industrial applications.
The life of an oil-free air compressor is significantly longer than an oil-lubricated counterpart. These models can operate up to 2,000 hours, four times longer than the average oil-lubed compressor. Oil-free compressors also have a significantly lower operating noise than their oil-lubricated counterparts. And because they don’t need oil changes, they are quieter. Some even last up to 2,000 hours.
An oil-free air compressor is a good choice if your application requires high levels of purity. Several applications require ultra-pure air, and even a drop of oil can cause product spoilage or damage to production equipment. In addition to the health risks, an oil-free air compressor reduces the costs associated with oil contamination and minimizes leaks. It also eliminates the need for oil collection, disposal, and treatment.
A typical oil-free air compressor is very efficient, requiring only about 18% of the full load horsepower. However, oil-free compressors have a higher risk of premature failure and are not recommended for large-scale industrial applications. They may also use up to 18% of the compressor’s full capacity. They may sound appealing, but you must make sure you understand the benefits of an oil-free air compressor before choosing one for your industrial applications.
Single-stage
A single-stage air compressor is designed to provide the power for a single pneumatic tool or device. These machines are generally smaller than two-stage compressors and produce less heat and energy. These machines aren’t designed for heavy-duty industries, but they are still highly effective for a variety of applications, including auto shops, gas stations, and various manufacturing plants. They can also be used in borewells, as they are suitable for small spaces with low air flow requirements.
A single-stage air compressor has one cylinder and two valves – the inlet and the delivery valves. Both of these valves function mechanically, with the inlet valve controlling torque and the delivery one controlling air pressure. Generally, single-stage compressors are powered by a gas engine, but there are also electric models available. The single-stage air compressor is the most common type of air compressor. It has a single cylinder, one piston, and one air cylinder.
The single-stage air compressors are used for small projects or personal use. A two-stage air compressor is more effective for industrial projects. Its longer air end life makes it more efficient. It is also more efficient for use in the automotive industry, where the engine has many cylinders. In general, single-stage compressors require a higher power level. The single-stage model is ideal for small projects, while a two-stage one is suitable for larger-scale arsenals.
CFM
The cubic foot-per-minute (CFM) of an air compressor is the output of the machine. In order to calculate the CFM level, start by looking at the compressor’s specifications. You should know how many cubic feet the unit can hold and how many pounds per square inch it can compress. Once you have these information, you can calculate the CFM. Now you can use these numbers to select an appropriate air compressor for your needs.
The most common way to increase the CFM of an air compressor is to turn the regulator down. By turning the dial down, the air compressor will produce more than 10 CFM. You can also try connecting two output valves. Make sure that the settings are adjusted properly before you begin. This will ensure that your air compressor is functioning at its maximum efficiency and lifespan. To increase the CFM of your air compressor, first check that your regulator is calibrated for the desired pressure level.
To calculate the CFM of an air compressor, first determine the tank volume of the machine. Then, multiply this volume by the time it takes to fill the tank. Then, divide the result by 60 seconds to calculate the CFM. Once you know how much air your machine can hold, you can choose a suitable air compressor. If you’re working in a confined area, you should buy a tool with a large tank.
PSI
The PSI of an air compressor is the pressure that it can output. A typical air compressor has a gauge connected to the airline at the bottom, next to it, or between the two. The gauge tells the actual pressure of the air compressor, while the cut-out pressure is determined by the manufacturer. The manufacturer recommends that you set the cut-out pressure twenty to forty PSI higher than the factory recommended pressure. If you want to set the pressure for your nail gun, you can use the cut-in and cut-out pressures on your compressor, and the tank won’t exceed this range.
The PSI of an air compressor measures the force that it can deliver, which is often in pounds per square inch. For most air tools, you need at least forty to 90 psi. In general, reciprocating air compressors work on an on/off basis. This relationship is known as the duty cycle. All air compressors are rated for a particular duty cycle, such as fifty percent on and twenty-five percent off.
The Psig of an air compressor is not free, as many people believe. The PSI of an air compressor is not free, but it is essential to maintain it for safe operations. If you’re having trouble maintaining a consistent pressure, consider turning down the PSI of your compressor by 2 psig. This will determine the critical pressure for the machine. You’ll also increase the amount of energy in the system by one percent.
Power source
The power source for an air compressor is crucial in its operation. Without the correct voltage and amperage, air compressors will not function properly. The power source must be close to the compressor so that it can plug into an electrical outlet. If it is too far from the outlet, the compressor may not be able to build enough pressure. When this happens, the fuse inside the air compressor will turn off to protect the user. The power source should be a safe distance from the compressor.
Most manufacturers do not specify the power source for an air compressor. Depending on the horsepower, the compressor will require approximately four amps of power. A one-horsepower compressor would draw about twelve amps. If it were powered by a typical 120-volt household supply, its motor would exceed the 15-amp breaker capacity. A larger air compressor, however, will require a separate 15-amp power source, making it impossible to use it with this type of power source.
The power source for an air compressor is typically electrical alternating current (AC) that is equivalent to the voltage on a standard wall outlet. A three-phase air compressor, on the other hand, requires a special AC supply with three electrical offset pulses. Regardless of the type of air compressor, the power source must be compatible with the incoming power service. One of the most common problems when attempting to connect an air compressor to an AC power source is undersized wire. This results in low voltage and high amperes, tripping of over-load relays and blown fuses.


editor by czh 2023-01-30